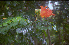Species Description
The African tulip tree is described as follows a \"large tree with a stout, tapering often somewhat buttressed trunk, branches thickish, marked with small white lenticels, subglabrous to thinly puberulent, reaches heights of 25 m; leaves usually opposite (rarely 3 at a node), very widely diverging, up to 50cm long, (7-) 11-15 (-17) leaflets broadly elliptic or ovate, entire, to 15 x 7.5cm, with 7-8 principal veins on each side, puberulent and prominent beneath, apex very slightly acuminate, base somewhat asymmetrically obtuse, lower leaflets tending to be reflexed, petiolule short, 2-3mm, rachis nearly straight, brownish-puberulent, petiole up to 6cm long, thickened at base; raceme 8-10cm long on a peduncle of about the same length, with a pair of reduced leaves about halfway up, rachis and pedicels thick, brownish puberulent, bracts subtending pedicels lanceolate, curved, about 1cm long, caducous, pair of bractlets near summit of pedicel similar, opposite; calyx strongly curved upward, asymmetric, about 5cm long, tapering, somewhat ribbed, splitting at anthesis to within a fewmm of base along dorsal curve, apex horn-like, blunt, exterior brownish sericeous puberulent; corolla bright vermilion or scarlet, 10-12cm long, mouth of limb about 7cm across, lobes about 3cm long, obtuse, margins strongly crispate, orange-yellow; filaments about 5cm long, dull orange anthers arcuate, linear, very dark brown, 15mm long; style yellow, 8cm long, stigma reddish; capsule lanceolate, slightly compressed, 17-25 x 3.5-7cm\" (Fosberg et al, 1993, in PIER, 2002).
Notes
The trunks and limbs of the African tulip tree are weak and don't stand up to typhoons very well, branches also break off easily as the tree gets older (PIER, 2002). The seedlings establish rapidly and the tree grows quickly, making it one of the first trees to colonise wastelands (Tan, 2001).
Uses
The seeds are edible. In Singapore the timber is used for making paper. In West Africa the wood is used to make drums and blacksmith's bellows. The bark, flowers and leaves are also used in traditional medicine in its native home range. (Tan, 2001)
The wood is difficult to burn and so the tree can be used in fire resistant landscaping. Buds contain liquid that will squirt out if they are squeezed or pierced, which children enjoy using as water pistols. African hunters are said to have boiled the seeds to extract arrow poison. (Floridata.com L.C. Copyright 1996 - 2002)
Habitat Description
The African tulip tree invades both abandoned agricultural land and closed forest; it invades natural ecosystems in the Cook Islands, Fiji, Guam, Hawai‘I, Samoa and Vanuatu (PIER, 2002; Labrada, pers.comm. 25 February 2003). Although the African tulip tree favours moist and wet areas below 1000m (Smith, 1985, in PIER, 2002), it grows upto 1,200m in French Polynesia (PIER, 2002).
The tulip tree does not tolerate frost and demands full sun for fast growth and best flowering. The biggest trees grow in moist sheltered ravines. This species loves rich soil, but puts up with just about anything with a little fertility to it, including limerock. It will survive a bit of salinity. (Floridata.com L.C. Copyright 1996 - 2002)
Reproduction
The flowers are pollinated by birds and bats and the seed is dispersed by the wind (Floridata.com L.C. Copyright 1996 - 2002). This plant is also capable of propagating by root suckers and cuttings (PIER, 2002), as well as by seed in cultivation. Each seed pod contains about 500 tissue papery seeds, (Floridata.com L.C. Copyright 1996 - 2002).
Principal source: Pacific Island Ecosystem at Risk (PIER), 2010. Spathodea campanulata P.Beauv., Bignoniaceae
Ricardo Labrada, pers. comm. 25 February 2003.
Compiler: IUCN SSC Invasive Species Specialist Group
Updates with support from the Overseas Territories Environmental Programme (OTEP) project XOT603, a joint project with the Cayman Islands Government - Department of Environment
Review: Ricardo Labrada Ph. D. FAO Plant Protection Service.
Publication date: 2010-10-04
Recommended citation: Global Invasive Species Database (2025) Species profile: Spathodea campanulata. Downloaded from http://iucngisd.org/gisd/species.php?sc=75 on 25-10-2025.