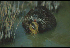- General
- Distribution
- Impact
- Management
- Bibliography
- Contact
Principal source: Woods, C.A., Contreras, L., Willner-Chapman, G. and Whidden, H.P. 1992. Myocastor coypus. Mammalian Species 398: 1-8.,
Carter, J. and Leonard, B. 2002. A review of the literature on the worldwide distribution, spread of and efforts to eradicated the coypu (Myocastor coypus). Wildlife Society Bulletin 30: 162-175.
Compiler: Dr. Sandro Bertolino, DIVAPRA Entomology and Zoology, University of Turin, Italy & IUCN/SSC Invasive Species Specialist Group (ISSG)
Review:
Publication date: 2008-04-13
Recommended citation: Global Invasive Species Database (2026) Species profile: Myocastor coypus. Downloaded from http://iucngisd.org/gisd/speciesname/Myocastor+coypus on 05-01-2026.
At high densities coypu are able to convert marshland to open water by feeding on plants. Habitat destruction caused by coypu threatens rare marshland species of bird, fish and invertebrates. In Italy coypu have caused breeding whiskered tern (Chlidonias hybrida) to decline by largely destroying the cover of water-lilies Nymphaea in Valli di Argenta a designated IBA (Important Bird Area). The habitats of two national treasure species in Japan - a critically endangered dragon fly (see Libellula angelina in IUCN Red List of Threatened Species) and a fish the vulnerable deep-bodied bitterling (see Acheilognathus longipinnis in IUCN Red List of Threatened Species) (Shirow Tatsuzawa, pers. Comm.) are threatened by coypu.
Coypu also feed on agricultural crops (Carter and Leonard 2002) including sugarcane, alfalfa and root crops (Woods et al. 1992)